Elliptic Curve Cryptography
April 18, 2023
What is cryptography?
Cryptography is the science and practice of securing communication through the use of mathematical algorithms and protocols to transform plain text into a secret code or cipher, making it unreadable without the proper key or password.
Now that we have the mundane definition out of the way we can focus on more mathematical stuff. This post builds upon the fact that you know the basic mechanism of encryption/decryption and have a working understanding of RSA. If you want a refresher, you can watch an amazing explanation by computerphile.
What is an Elliptic Curve
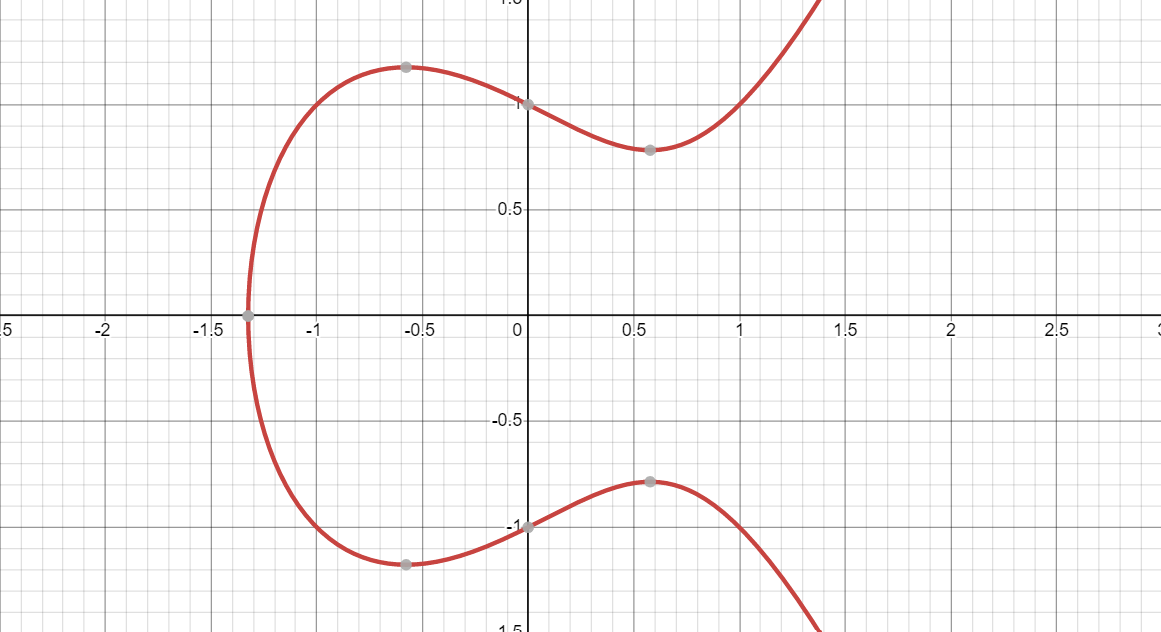
Any equation of the form y2 = x3 + ax + b; where a, b ∈ R
Looks something like this:
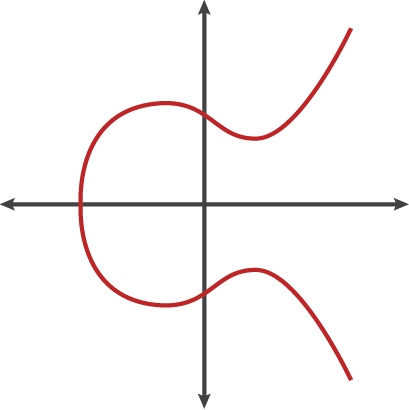
It has some cool properties like horizontal symmetry and any non-vertical line will intersect the curve at most 3 points.
Weird game of bounce
Let's imagine a simple game. We start at any point in the elliptic curve and consider any other point on the curve. If selected with care a line joining these 2 points will intersect the curve at point 3. Now this 3rd point is the dot product of these 2 points. Well not exactly, cause A ⋅ B = -C. We just reflect the point horizontally and get C. Now we just gotta do this operation again with A and C, and then repeat this finite many times. If we take the point A as the starting point and dot product it with itself, we'll get a tangent at that point. These are some properties of ecceptic curve, we'll dwell into them later.
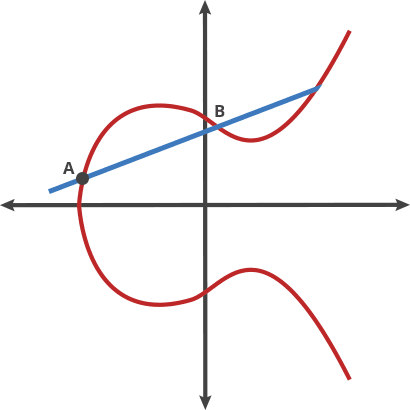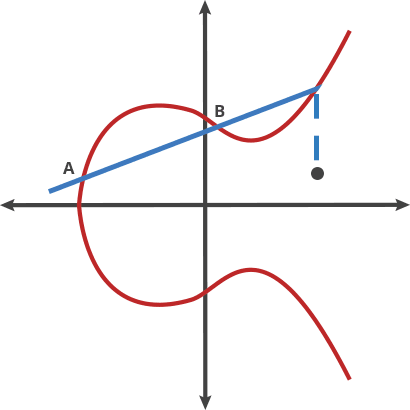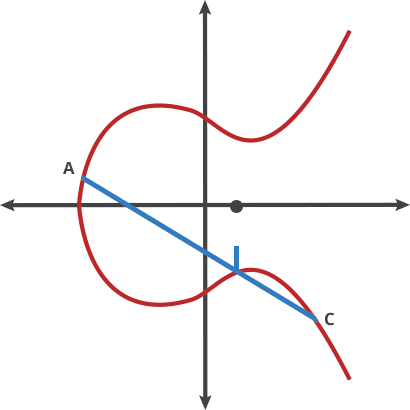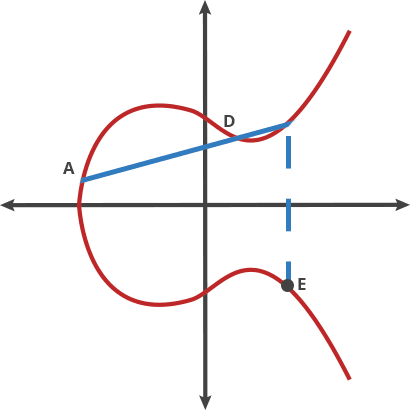
What do we have so far?
We had a starting point A, and then we made it do a thing n times to get a new point Z. Now comes the fun part! Let's suppose you know A and you know Z but there is no way you can find n without doing the above operation. This forms a very effective Trapdoor function.
Let's go deep

The simple example above is great to understand things, but we need a special kind of curve to work in our cryptographic system. We will restrict ourselves to whole numbers in a fixed range. We will roll over the number (aka take mod) when we go out of our range and take this maximum as a prime number.
If we are to understand it with and example, let's suppose we have the curve y^2 = x^3 - x + 1 we get:
If we choose the maximum as 97 then we get:
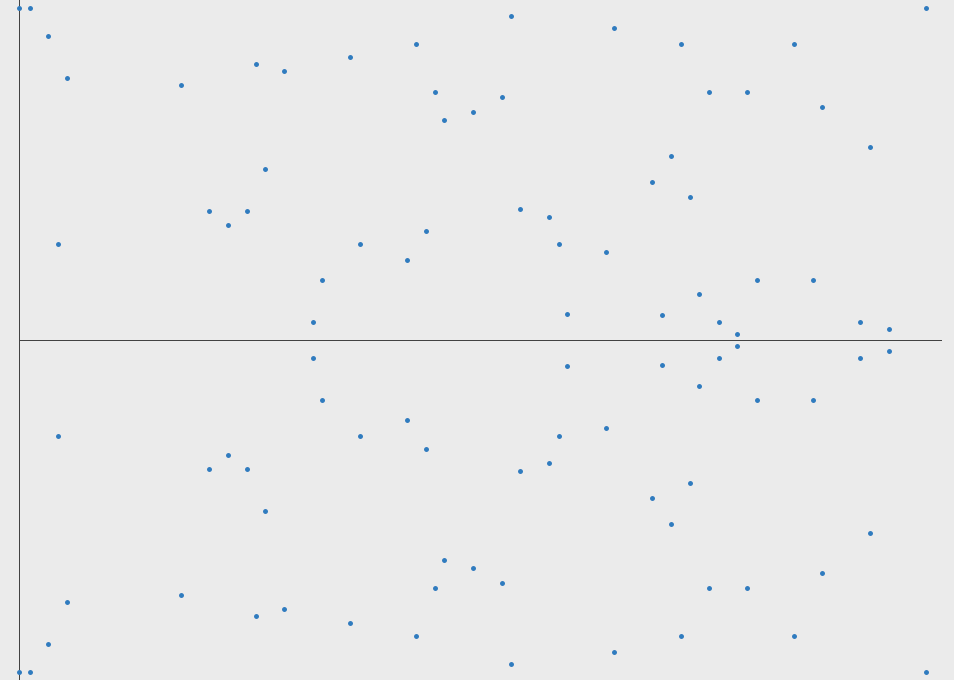
As you can observe it still resembles the original curve just with some restrictions. It has retained its horizontal symmetry. It even has the properties of dot product intact as it is a subset of the original curve.

Piecing it all together
Now we have everything, let's glue the pieces together. To create a cryptography system we will define a prime number as a maximum (it is generally a Mersenne prime), a curve equation and a public point on the curve. A private key PK is a number, and the public key is the public point dotted itself PK times. Computing PK from the public key in this system is called the elliptic curve discrete logarithm function. Researchers haven't got any major breakthrough in solving this apart from the convention mechanism and it has proved to be quite robust against any heuristic solutions. In layman's terms, there doesn't appear to be a shortcut that narrows the gap in a Trapdoor Function based on this problem.
This can now be used to encrypt the data by selecting the appropriate public key, private key and curve equation.
Advantages
- Shorter key lengths: ECC provides the same level of security with shorter key lengths than RSA. For example, a 256-bit ECC key provides the same level of security as a 3072-bit RSA key. To put this into perspective, breaking a 228-bit RSA key requires less energy than it takes to boil a teaspoon of water. Comparatively, breaking a 228-bit elliptic curve key requires enough energy to boil all the water on Earth.[1]
- Faster Performance: ECC requires less processing power and memory, making it ideal for low-power devices, such as smartphones and IoT devices.
The downside
It is not all roses in the world of elliptic curves, there have been tremors of distrust in the researchers. A RNG standardized by NIST and promoted by NSA Dual_EC_DRBG, has been suspected of being designed with a backdoor. There has been progress in developing curves with efficient arithmetic outside of NIST, including curve 25519 created by Daniel Bernstein.
Applications
It is used by cloudflare for secure communication protocols, such as SSL/TLS, SSH, and IPSec. Widely used in mobile devices due to limited processing power and memory. It is the backbone behind Bitcoin and some other cryptos for digital signatures. It is used in your Teslas and iMessage service for secure comms.
[1] Universal security from bits and mips to pools, lakes - and beyond Credits: Cloudflare blog
