Key Management Server
October 08, 2023
Key Management
Let's get the basics straight! Why do we even need keys, and what the hell is key management? Why do we need servers to manage them? And should you even worry about this?
Every information on the internet is valuable for the right use case therefore companies invest large amounts to securely store and encrypt all the information they have. The encryption is to ensure data confidentiality even in the case of a data breach. All our information is not stored as plain text on the internet, it is stored in some sort of encoded language that means absolute gibberish when viewed in isolation. We need to decrypt this information to make any sense of it.
We need keys to do the encryption; you can imagine keys as the secret ingredient that makes the plain text into gibberish and you need the same key to turn that gibberish into any meaningful information (aka back to plain text). Thus keys are super important, and we need a robust system to handle all our keys. For eg. we can see we are encrypting the text and then decrypting it using the same key. Generally, these keys are quite huge, exactly 256 bits (that is a number that could be 77 digits long)
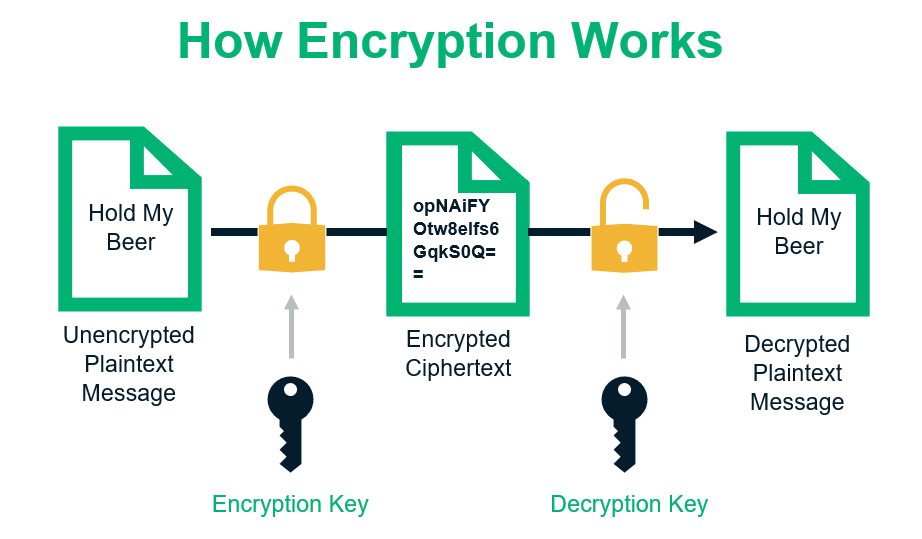
Now let's increase the level of security and say we want our keys to be generated, rotated, stored, and expired all automatically. This needs Key Management software!
Key management is the process of managing cryptographic keys throughout their lifecycle, from generation to destruction. This includes:
- Key generation: Generating strong cryptographic keys that are resistant to attack.
- Key storage: Storing keys in a secure manner that protects them from unauthorized access and compromise.
- Key distribution: Distributing keys to authorized users and applications in a secure manner.
- Key rotation: Rotating keys on a regular basis to reduce the risk of compromise.
- Key destruction: Destroying keys securely when they are no longer needed.
Key Management Server
A key management server (KMS) is a system for securely storing, managing and backing up cryptographic keys. KMSs are used to protect a wide variety of data, including encryption keys, digital certificates, and API keys. KMSs typically provide a variety of features to help organizations manage their keys, including:
- Key generation and rotation: KMSs can generate strong cryptographic keys and rotate them regularly to help protect them from compromise.
- Secure key storage: KMSs store keys in a secure manner using encryption and other security measures.
- Key access control: KMSs allow organizations to control who has access to which keys and what operations they can perform on them.
- Key auditing: KMSs provide audit logs to help organizations track who has accessed their keys and what they have done with them.
- Policy management: Policy management is what allows an individual to add and adjust these capabilities. For example, by setting policies on encryption keys, a company can revoke, expire, or prevent the sharing of the encryption keys, and thus of the unencrypted data, too.
- Authentication: This is needed to verify that the person given a decryption key should be allowed to receive it. When encrypting digital content, there are several ways to achieve this.
- Authorization: It's the process that enforces encryption key policies and ensures that the encrypted content creator has control of the data that's been shared.
- Key transmission: This is the final step in the overall encryption key management process and is related to how keys get transmitted to the people who need them, yet still restrict access to those who don't.
Key Management Advantages
- Improved security: KMSs help to improve the security of data by storing and managing cryptographic keys in a central location. This makes it more difficult for attackers to compromise keys and access sensitive data.
- Reduced risk: KMSs can help to reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents by providing a centralized system for managing keys. This makes it easier to keep track of keys and ensure that they are being used properly.
- Compliance: KMSs can help organizations comply with industry regulations and standards that require the use of strong cryptographic keys.
- Operational efficiency: KMSs can help to improve operational efficiency by automating the process of key generation, rotation, and management.
Hardware Security Modules
A hardware security module (HSM) is typically a physical piece of hardware that handles key storage and cryptographic functions at scale. (There are some cloud HSMs available as well but the term HSM typically refers to the physical devices.) An HSM is a secure environment that allows you to handle key lifecycle management operations and offload many cryptographic operations as well. (This way, you're not overburdening your servers and other systems.)
Key management servers also communicated with HSMs on their backends to provide secure storage and backups. They also typically enable you to carry out limited cryptographic operations as well. For example, some key management systems will allow you to use the keys inside the KMS to perform data signing and other related functions.
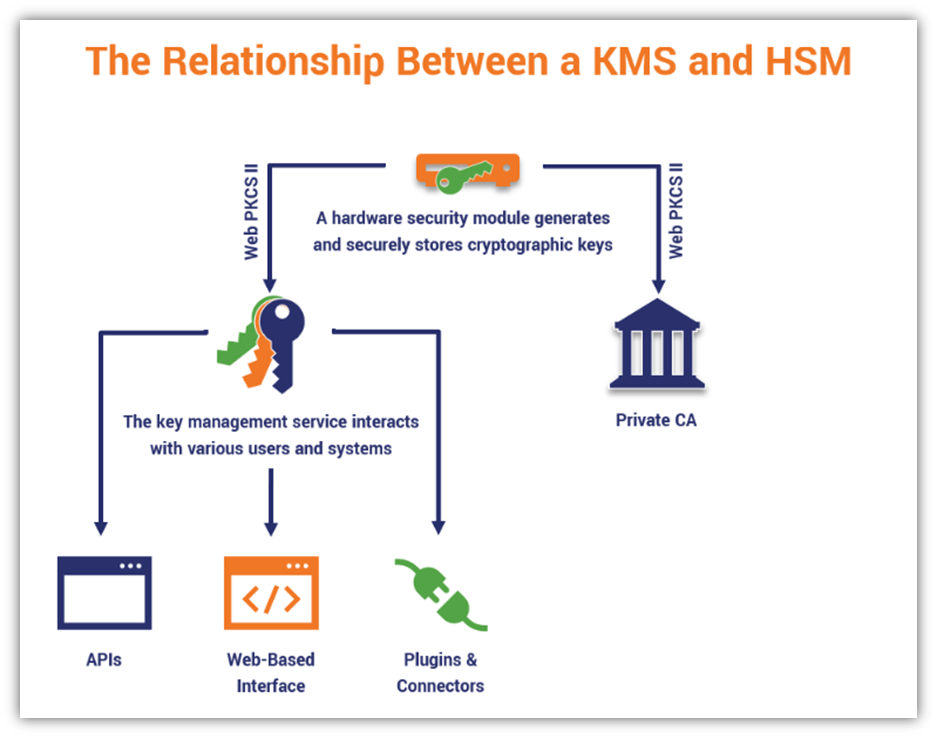 A basic illustration that shows the relationship between a KMS and a HMS.
A basic illustration that shows the relationship between a KMS and a HMS.
Key Management on an Enterprise scale
Key management is essential for large organizations because they typically have large amounts of sensitive data that need to be protected. This data can include customer records, financial information, and intellectual property. Large organizations use KMS to Protect their data from unauthorized access and compromise Key management is essential for large organizations because they typically have large amounts of sensitive data that need to be protected. This data can include customer records, financial information, and intellectual property. Large organizations use KMS to
- Protect their data from unauthorized access and compromise
- Comply with industry regulations and standards
- Improve operational efficiency
Key management is an essential tool for large organizations that need to protect their data. By using a key management system, organizations can improve the security of their data, reduce the risk of data breaches, and comply with industry regulations. Additional benefits like digital signatures and encryption of private information are also covered by almost all the enterprise solutions offered in the industry.
There are two main types of KMSs: on-premises KMSs and cloud-based KMSs. On-premises KMSs are typically deployed in a customer's own data center. Cloud-based KMSs are hosted by a cloud provider, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
Here are some examples of how large organizations use KMSs to protect their data:
- AWS KMS: AWS KMS is a cloud-based KMS that is used by millions of organizations around the world to protect their data. AWS KMS is used by organizations of all sizes, including Fortune 500 companies, government agencies, and startups.
- Azure Key Vault: Azure Key Vault is a cloud-based KMS that is offered by Microsoft Azure. Azure Key Vault is used by organizations of all sizes to protect their data, including Fortune 500 companies, government agencies, and startups.
- Google Cloud KMS: Google Cloud KMS is a cloud-based KMS that is offered by Google Cloud Platform. Google Cloud KMS is used by organizations of all sizes to protect their data, including Fortune 500 companies, government agencies, and startups.
Conclusion
KMSs are essential tools for organizations of all sizes that need to protect their data. By using a KMS, organizations can improve the security of their data, reduce the risk of data breaches, and comply with industry regulations.
